I've been treating people with Type 2 diabetes for over 15 years, and I want to share what I've learned from working with thousands of patients. This condition doesn't have to define your life—with the right knowledge and support, you can absolutely thrive.
What Type 2 Diabetes Really Means
When I first meet someone who's been diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes, they often feel overwhelmed and scared. I get it—I've been there myself when my own family members were diagnosed. But here's what I want you to know: this condition is manageable, and many of my patients live incredibly full, healthy lives.
Type 2 diabetes affects how your body processes blood sugar, but it's not a life sentence. I've seen patients who've reversed their condition through lifestyle changes, and others who've managed it so well that it barely affects their daily routine.
Key Facts About Type 2 Diabetes
- Most common form of diabetes
- Usually develops in adults over 45
- Often preventable with lifestyle changes
- Manageable with proper care
Symptoms and Warning Signs
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Frequent infections
Risk Factors
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Excess weight, especially around the waist
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Smoking
Non-modifiable Risk Factors
- Age (45 years or older)
- Family history
- Race and ethnicity
- History of gestational diabetes
Management Strategies
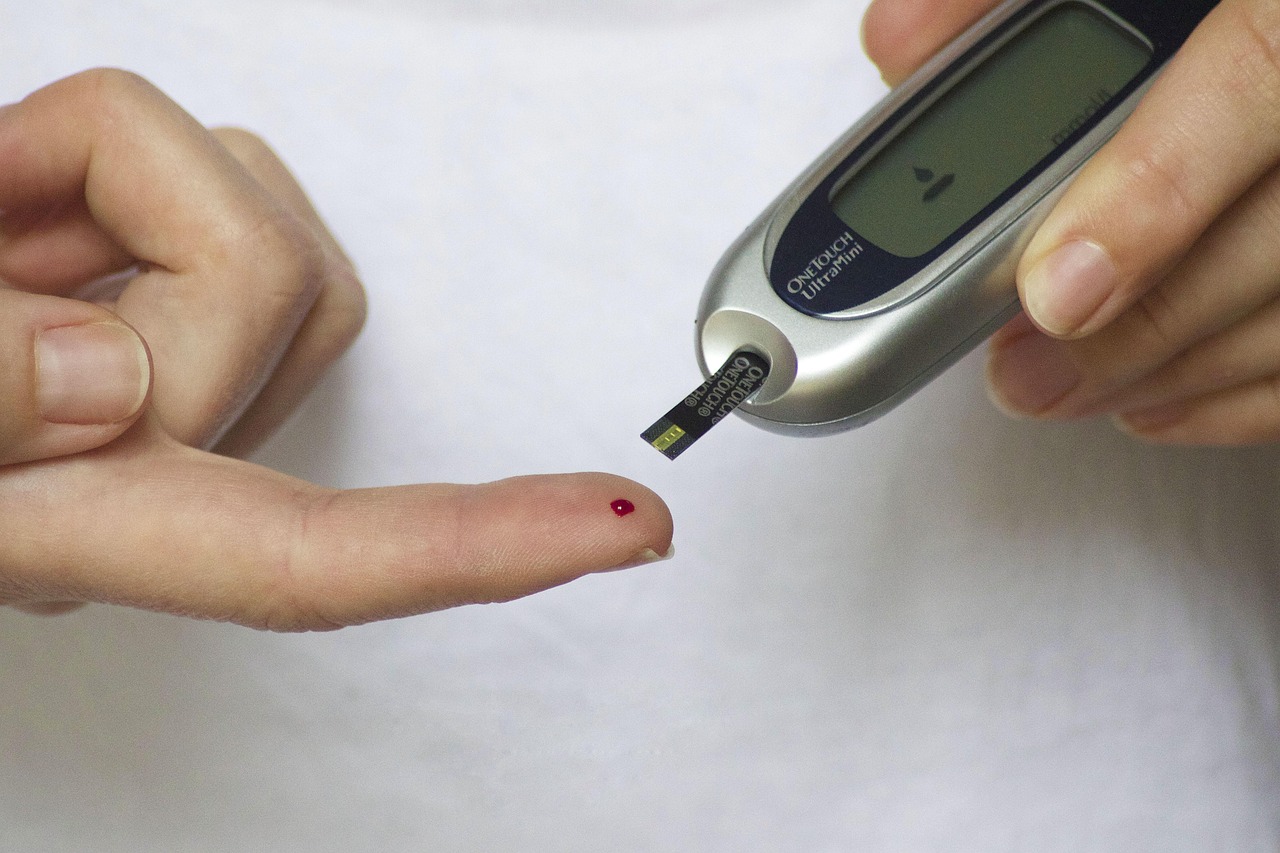
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring helps you understand how food, activity, stress, and medication affect your blood sugar levels.
Healthy Eating
- Focus on whole foods
- Control portion sizes
- Limit refined sugars and carbs
- Include plenty of vegetables
Regular Exercise
- Aim for 150 minutes of moderate activity per week
- Include both aerobic and strength training
- Start slowly and build up gradually
- Check blood sugar before and after exercise
Medical Treatment
Treatment may include medications such as:
- Metformin (first-line treatment)
- Sulfonylureas
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- GLP-1 receptor agonists
- Insulin (if needed)
Complications Prevention
Proper management helps prevent serious complications:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Kidney damage
- Eye problems
- Nerve damage
- Foot problems
Regular Check-ups
Work closely with your healthcare team and maintain regular appointments for optimal diabetes management.